Auditing is a means of evaluating the effectiveness of a
company's internal controls. Maintaining an effective system of internal
controls is important for any organization for achieving its business
objectives, better clientele, preventing fraud, misappropriation of its assets
& compliance with laws and regulations. Audits are used to gather facts and
determine the degree to which requirements are being met. It is based on the
Deming cycle or PDCA model used for continuous improvement of quality. It
consists of a logical sequence of 4 repetitive steps for continuous improvement
as shown:
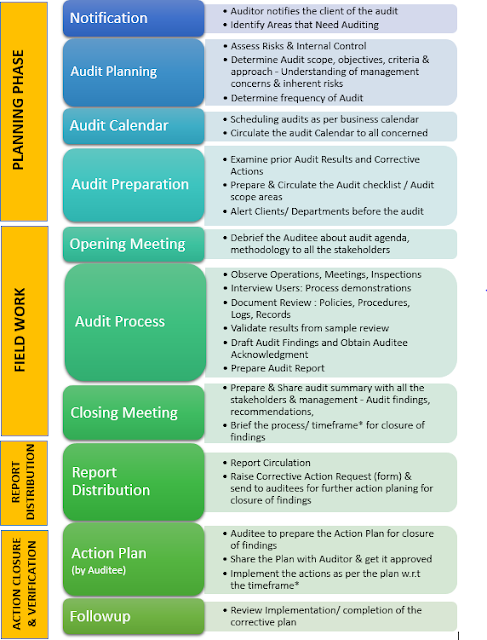
Audit
process flow & further briefing the process associated with it, is shown
below:
Audit report & its elements:
An audit report may have an ‘Audit scope
& purpose, executive summary, description including the specific issues or
findings identified and related recommendations/ action plans’ etc. Each audit
finding within the report may contain five elements, sometimes referred as the
"5 C's":
Condition: What is the
particular problem identified?
Criteria: What is the standard that was not met? The standard
may be a standard requirement, company policy or other benchmark.
Cause: Why did the
problem occur?
Consequence: What is the risk/negative outcome because of the
finding?
Corrective action: What the management agreed to do to rectify or close
the problem founded and by when?
In any
audit, there are generally 5 categories of findings.
Categories of Audit Findings:
As a common practice among various
organizations, there are 5 categories of findings
- Minor Non-Conformance - Are the areas where element of the standard requirement are partially met or there is minor lapse in the quality management system w.r.t the requirement. Action Planning is required for closure.
- Major Non-Conformance - Are the areas where an element of the standard requirement has not been met or where there is a significant breakdown in the quality management system. Also, a group of Minor Non-Conformance in the same specific area of the standard may also be elevated to this category. Action Planning is required for closure.
- Observation - Observation are the potential non-conformance or can be said as areas currently being in compliance but very close to becoming a non-conformance, if adequate actions are not taken. Observations can be looked as “accidents waiting to happen”. Action Planning is required for closure.
- Opportunity for Improvement - Unlike observations, opportunity for improvement are not accidents waiting to happen but rather these are practices that have been poorly implemented i.e either ineffective or consist of several non-value added steps. Usually action planning is not required to be reported but good to have a planned closure.
- Strength or Noteworthy efforts - Are the areas observed during the audit having excellent examples of implementation w.r.t the requirements of the standard. These are basically given to the bench-marking or best in class practices.
6.
Time frame for closure of Non-Conformance:
Internal Audit:
As a
process, once a ‘Corrective Action
Request’ is raised by auditor, auditee needs to submit the ‘Action Plan’ comprising of Root Cause
Analysis(RCA), Corrective actions(CA), Preventive Actions(PA), responsible person against each of them &
timelines or due date for its implementation. This timeline has to be an agreed
one between the auditee & auditor.
Once the
action is implemented & due date for implementation of actions is over,
auditor needs to review the implementation & its effectiveness within 90
days after implementation.
External
Audit: (Standard time frame is followed)
If a Minor NC is raised,
- ‘Root Cause Analysis’ along with proposed ‘Corrective Action Plan’ is required within 90 days of the audit.
- Implementation of plan i.e Corrective/ Preventive actions should be completed within 12 months after the audit.
- Review of implementation should be done, at the latest.
If a Major NC is raised,
- ‘Root Cause Analysis’ along with proposed ‘Corrective Action Plan’ is required within 7 days of the audit.
- Implementation of plan i.e Corrective/ Preventive actions should be completed within 30 days after the audit
- Review of implementation should be done, at the latest.
Those businesses
are considered successful which has the ability to deliver their products and services accurately & seamlessly, as well as meet the needs of their
customers. Internal audit is a tool that organizations use to ensure that their
products and services are delivered the right way, the first time and every
time.

Title is Internal Audit, but lot is talked about external audit. Categorizations of NCs in internal audit is not called for and leads to more confusion. All noncompliance are NC and need actions. External Audit has some restrictions in issue of certifications with more no of NCs and major NCs which internal auditor do not have.
ReplyDeleteThis blog helps me to get some detailed info. Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeleteISO 9001 internal auditor course
I came onto your blog while focusing just slightly submits. Nice strategy for next, I will be bookmarking at once seize your complete rises... Project Management Services
ReplyDelete